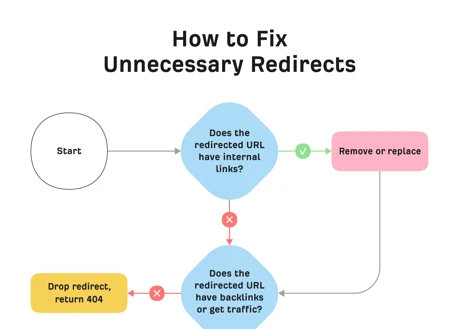
No, non-indexed pages cannot receive organic traffic because search engines are unable to include them in their search results.
Understanding the Issue

There can be several reasons why certain webpages are not being indexed by search engines. One common reason is technical issues such as server errors, incorrect use of robots.txt file, or noindex tags mistakenly applied to the page. Another reason could be that the webpage is new and hasn’t been crawled by search engine bots yet. Additionally, if the content on the page is deemed low-quality or duplicate, search engines may choose not to index it. It’s important to identify the specific reason behind non-indexed pages in order to address the issue effectively.
Non-indexed pages can have a significant impact on your website’s SEO. When a page is not indexed, it means that search engines are not aware of its existence. As a result, the page won’t show up in search engine results pages (SERPs), making it difficult for users to find your content. This can lead to a decrease in organic traffic and hinder your website’s visibility. Non-indexed pages also prevent search engines from understanding the full scope of your website’s content and can negatively affect your overall website authority. It is crucial to address this issue promptly to ensure that your webpages are being properly indexed and contributing to your SEO efforts.
1. Reasons for Pages Not Being Indexed
There are various reasons why certain webpages may not be indexed by search engines. Understanding these reasons is crucial in order to address the issue effectively. Here are some common reasons for pages not being indexed:
1. Technical Issues: These include server errors, incorrect use of the robots.txt file, or the presence of noindex tags on the page. These issues prevent search engine bots from accessing and indexing the page.
2. New Webpage: If a webpage is new, it may not have been crawled by search engine bots yet. It takes time for search engines to discover and index new pages.
3. Low-Quality or Duplicate Content: Pages with low-quality or duplicate content may not be indexed by search engines. Search engines prioritize high-quality and unique content to provide the best user experience.
4. Blocked by URL Parameters: If a webpage has URL parameters that are blocked from indexing, search engines may not be able to crawl and index the page properly.
5. Canonicalization Issues: Canonicalization refers to the process of selecting the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple versions available. If canonical tags are not properly implemented, search engines may not index the desired version of the page.
By understanding these reasons, you can identify the specific issue causing your pages to not be indexed and take the necessary steps to resolve it.
2. Impact of Non-Indexed Pages on SEO
The impact of non-indexed pages on SEO can be detrimental to your website’s overall performance. When a page is not indexed by search engines, it means that it is not included in the search engine’s database and therefore will not appear in search engine results pages (SERPs). This lack of visibility can severely limit the organic traffic your website receives, as users won’t be able to find your content through search queries. Non-indexed pages also prevent search engines from understanding the full scope of your website’s content, which can negatively impact your website’s authority and ranking.
Having non-indexed pages can also hinder your website’s ability to attract backlinks, as other websites may not be aware of the existence of your content. Backlinks are an important factor in SEO, as they signal to search engines that your website is reputable and valuable. Without indexed pages, it becomes difficult for other websites to discover your content and link to it, which can hinder your overall SEO efforts.
Non-indexed pages can lead to a poor user experience. When users search for specific information or keywords related to your website, they expect to find relevant results. If your webpages are not indexed, users will not be able to find the content they are looking for, which can result in frustration and dissatisfaction. This can ultimately impact your website’s reputation and user engagement.
To ensure that your website is optimized for search engine visibility and to maximize your SEO efforts, it is crucial to address and fix any non-indexed pages promptly. By doing so, you can improve your website’s organic traffic, visibility, and overall performance in search engine rankings.
Identifying Non-Indexed Pages

Identifying non-indexed pages is the first step in resolving the issue. One way to do this is by using Google Search Console. This tool provides valuable insights into your website’s performance and indexing status. Within Search Console, you can navigate to the Index Coverage report to see a list of pages that are not indexed. This report will show you the specific reasons why each page is not being indexed, such as crawl errors or noindex tags. By analyzing this information, you can prioritize which pages need immediate attention.
For larger websites, crawling tools can be beneficial in identifying non-indexed pages. These tools, such as Screaming Frog or DeepCrawl, crawl your entire website and provide comprehensive reports on indexing status. They can help you identify any technical issues that may be preventing search engines from indexing your pages. These tools also provide insights into other SEO factors like broken links, duplicate content, or missing meta tags, which can further impact your website’s indexing and overall performance.
By utilizing Google Search Console and crawling tools, you can efficiently identify non-indexed pages on your website and gain a deeper understanding of the underlying issues that need to be addressed. This knowledge will allow you to move forward with the necessary steps to resolve the problem and improve your website’s visibility in search engine results.
1. Using Google Search Console
Using Google Search Console is an effective way to identify non-indexed pages on your website. Start by logging into your Google Search Console account and selecting your website property. Then, navigate to the “Coverage” report under the “Index” section. This report will provide you with information on the indexing status of your webpages. Look for any pages that are labeled as “Crawled – currently not indexed.” These are the pages that need to be addressed.
To further investigate the issue, click on the specific page URL from the report. Google Search Console will provide details on why the page is not indexed. It could be due to crawling issues, such as server errors or robots.txt restrictions. Alternatively, it may be because the page contains a noindex tag, preventing search engines from indexing it.
Once you have identified the reason for non-indexing, take the necessary steps to fix the issue. For example, if it’s a crawling issue, ensure that your website is accessible to search engine bots and that your robots.txt file is properly configured. If the page has a noindex tag, remove or modify it to allow indexing.
Regularly checking the Coverage report in Google Search Console will help you stay updated on the indexing status of your webpages. This will allow you to address any non-indexed pages promptly and ensure that your website’s content is being properly indexed and visible to users.
2. Crawling Tools for Large Websites
When it comes to identifying non-indexed pages on larger websites, utilizing crawling tools can be extremely helpful. These tools are designed to crawl through your website and provide comprehensive reports on the status of each page. One popular crawling tool is Screaming Frog, which allows you to crawl up to 500 URLs for free. This tool provides valuable insights such as the HTTP status codes of each page, the number of internal and external links, and the presence of meta tags and canonical tags. Another useful tool is DeepCrawl, which is designed specifically for larger websites with thousands or even millions of pages. DeepCrawl provides detailed reports on crawling data, highlighting any issues that may be affecting the indexing of your pages. By using these crawling tools, you can efficiently identify non-indexed pages and take the necessary steps to resolve the issue. Remember, a well-optimized website that is fully indexed will greatly improve your chances of attracting organic traffic and boosting your SEO efforts.
Resolving the Issue
To resolve the issue of non-indexed pages, you need to take a two-fold approach: fixing technical issues and optimizing your content for indexing.
1. Fixing Technical Issues:
Identify and resolve any technical issues that may be preventing search engine bots from indexing your webpages. This includes checking for server errors, ensuring that your robots.txt file is properly configured to allow crawling, and removing any accidental noindex tags. Regularly monitor your website for any crawl errors using tools like Google Search Console or third-party crawling tools to identify and address any technical issues promptly.
2. Optimizing Content for Indexing:
Optimize your content to ensure that search engine bots can easily crawl and index your webpages. Start by conducting keyword research to identify relevant keywords and incorporate them strategically into your content, including the page title, headings, and body text. Make sure your content is unique, high-quality, and provides value to users. Avoid duplicate content and ensure that each page has a unique meta description. Additionally, optimize your images by providing descriptive alt text and using keyword-rich file names.
By addressing these technical issues and optimizing your content, you can improve the chances of your webpages being properly indexed by search engines and increase your website’s visibility in search results. Remember to regularly monitor and maintain your website to prevent any future indexing issues.
1. Fixing Technical Issues
To fix technical issues causing non-indexed pages, it is important to address the specific problems hindering search engine crawling and indexing. Start by checking for server errors or connectivity issues that may prevent search engine bots from accessing your webpages. Ensure that your robots.txt file is properly configured to allow search engine crawlers to index your content. If you have mistakenly applied a noindex tag to a page, remove it to allow search engines to index the page. Another technical issue to consider is the page load speed, as slow loading pages can negatively impact indexing. Optimize your website’s speed by compressing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, and leveraging browser caching. Additionally, ensure that your website has a sitemap.xml file in place, which helps search engines discover and crawl your pages more efficiently. By addressing these technical issues, you can improve the chances of your webpages being properly indexed and visible in search engine results.
2. Optimizing Content for Indexing
Optimizing your content is crucial in ensuring that your webpages get indexed by search engines. Here are some steps you can take to optimize your content for indexing:
1. Keyword research: Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant and high-volume keywords that are related to your content. Incorporate these keywords naturally throughout your webpage, including in the title, headings, meta tags, and within the body of the content. This will help search engines understand the context and relevance of your webpage.
2. High-quality and unique content: Create high-quality and unique content that provides value to your audience. Avoid duplicate content, as search engines prioritize original content. Make sure your content is comprehensive, engaging, and informative.
3. Optimize meta tags: Craft compelling meta titles and descriptions that accurately reflect the content on your webpage. Include relevant keywords in these meta tags to increase the visibility of your webpage in search engine results.
4. Structured data: Implement structured data markup on your webpage to provide additional information about your content to search engines. This can help search engines understand the context and relevance of your content, which may improve the chances of your webpage getting indexed.
5. Internal linking: Include internal links within your content to help search engines discover and crawl other pages on your website. Internal linking also helps establish a hierarchical structure and improves the overall user experience.
6. Optimize images: Use descriptive file names and alt tags for your images. This helps search engines understand the content of the image and can improve the visibility of your webpage in image search results. For more information on how to optimize images, you can refer to our guide on how to link photos.
By following these optimization techniques, you can increase the chances of your content being indexed by search engines and improve your website’s overall visibility and organic traffic.
Monitoring and Reindexing
Once you have resolved the issue of non-indexed pages, it is important to monitor the status of your indexed pages and ensure that they are being properly crawled and indexed by search engines. This will help you stay on top of any potential indexing issues that may arise in the future.
1. Monitoring Indexed Pages: Regularly checking the indexed pages of your website is essential to ensure that all your important content is being properly indexed. You can use tools like Google Search Console to keep track of the number of indexed pages and identify any sudden drops or inconsistencies. Monitoring indexed pages will help you identify any new non-indexed pages that may have slipped through the cracks and allow you to take immediate action to fix the issue.
2. Requesting Reindexing: If you have made significant changes to a page that was previously not indexed, or if you have fixed any technical issues that were hindering indexing, you can request search engines to reindex the page. This will prompt search engine bots to recrawl the page and update their index accordingly. In Google Search Console, you can use the URL Inspection tool to request reindexing for specific pages. Keep in mind that reindexing may take some time, so be patient and continue to monitor the status of your indexed pages.
By regularly monitoring indexed pages and requesting reindexing when necessary, you can ensure that your webpages are being properly crawled and indexed by search engines. This will help maintain a strong online presence and improve the visibility of your website in search engine results pages (SERPs).
1. Monitoring Indexed Pages
Monitoring indexed pages is essential to ensure that your webpages are being properly recognized and included in search engine results. By keeping track of your indexed pages, you can identify any potential issues and take appropriate actions. One way to monitor indexed pages is by using Google Search Console. This powerful tool provides valuable insights into how your website is performing in search results. Within the Search Console, you can navigate to the “Coverage” report to see the number of indexed pages on your site. This report will highlight any errors or issues that might be preventing certain pages from being indexed. By regularly checking this report, you can stay informed about the status of your indexed pages and address any problems that arise promptly. Additionally, you can use crawling tools like Screaming Frog or DeepCrawl to analyze your website and identify any pages that are not being indexed. These tools can provide detailed reports on the crawlability of your website and help you pinpoint any technical issues that may be affecting indexing. By regularly monitoring your indexed pages, you can ensure that your website is fully optimized for search engines and that all your valuable content is being properly recognized and displayed in search results.
2. Requesting Reindexing
Requesting reindexing is an important step in getting your non-indexed pages recognized by search engines. Once you have fixed any technical issues and optimized your content for indexing, you can request reindexing to ensure that the changes are reflected in search engine results. To do this, you can use the Google Search Console. Simply select the affected website property and navigate to the “URL Inspection” tool. Enter the URL of the non-indexed page and click the “Request Indexing” button. Google will then crawl the page again and update its index accordingly. It’s important to note that requesting reindexing does not guarantee immediate indexing, as search engines have their own algorithms and timelines for crawling and indexing webpages. However, it is an effective way to notify search engines about the changes made to the page and expedite the indexing process. By regularly monitoring indexed pages and requesting reindexing when necessary, you can ensure that your webpages are properly indexed and visible to users.
Preventing Future Issues
To prevent future issues with non-indexed pages, it is important to implement regular crawling and indexing checks. This involves regularly monitoring your website to ensure that all pages are being indexed by search engines. You can use tools like Google Search Console to keep track of any indexing errors or issues that may arise. Additionally, optimizing your XML sitemap can help improve the indexing process. Make sure that your sitemap is up-to-date, includes all relevant URLs, and follows Google’s guidelines for sitemap creation. By regularly checking and optimizing your website’s crawling and indexing process, you can minimize the chances of encountering non-indexed page issues in the future, ensuring that your content is easily discoverable by search engines and reaching a larger audience.
1. Regular Crawling and Indexing Checks
Regular crawling and indexing checks are essential in ensuring that all your webpages are being properly indexed by search engines. By regularly monitoring the indexing status of your pages, you can quickly identify any issues and take appropriate action. Here are some steps to follow for regular crawling and indexing checks:
1. Utilize Google Search Console: Google Search Console is a powerful tool that provides valuable insights into how your website is performing in search results. It allows you to view the indexing status of individual pages and identify any errors or issues. Regularly check the Index Coverage report in Search Console to ensure that all your important pages are being indexed correctly.
2. Set up Google Alerts: Google Alerts is a free service that sends you email notifications whenever your selected keywords or phrases appear in newly indexed webpages. By setting up alerts for your website’s important keywords, you can keep track of new pages being indexed by search engines. This can help you identify any indexing issues or potential duplicate content problems.
3. Perform manual searches: Conducting manual searches using relevant keywords can give you a good idea of how well your webpages are ranking in search results. Make sure to search for specific pages or content that you want to be indexed. If you notice that certain pages are not appearing in the search results, it could indicate an indexing issue that needs to be addressed.
4. Check XML sitemap: Your website’s XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your site and helps search engines understand its structure. Regularly check your XML sitemap to ensure that it includes all the important pages and that there are no errors or broken links. Submitting an updated sitemap to search engines can help them discover and index your pages more efficiently.
By regularly performing crawling and indexing checks, you can stay proactive in ensuring that all your webpages are being properly indexed. This will help improve your website’s visibility in search results and drive more organic traffic. Remember to monitor your indexing status regularly and address any issues promptly to maintain a healthy and well-indexed website.
Link anchor: unique visitors per month
2. XML Sitemap Optimization
Optimizing your XML sitemap can play a crucial role in ensuring that your webpages are being indexed by search engines effectively. An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the URLs on your website and provides additional information about each page, such as its last modified date and priority. Here are some key steps to optimize your XML sitemap:
1. Include all relevant pages: Make sure that your XML sitemap includes all the important pages on your website that you want search engines to index. This includes not only your main pages but also any subpages, blog posts, or product pages.
2. Remove non-indexable pages: Exclude any pages that you don’t want search engines to index, such as login pages, thank you pages, or duplicate content pages. This helps search engines focus on indexing the most valuable and unique content on your website.
3. Ensure proper formatting: Ensure that your XML sitemap is properly formatted according to the XML protocol. This includes using the correct tags and structure, as well as validating the sitemap using tools like XML validators.
4. Set priority and frequency: Use the “priority” and “changefreq” tags in your XML sitemap to indicate the relative importance and frequency of updates for each page. This helps search engines understand which pages to crawl and index more frequently.
5. Submit your sitemap to search engines: Once you have optimized your XML sitemap, submit it to search engines through their respective webmaster tools. This allows search engines to easily discover and crawl your webpages.
By optimizing your XML sitemap, you provide search engines with a clear roadmap of your website’s content, improving the chances of your webpages being indexed and ranked in search results. Don’t forget to regularly update your XML sitemap whenever you add or remove pages from your website to ensure accurate indexing. For more information on creating image links, check out our guide on how to create an image link.
Conclusion
In conclusion, discovering that some of your webpages are currently not indexed can be frustrating, but it’s important to understand the reasons behind this issue and take steps to resolve it. Technical issues, low-quality content, or the newness of the webpage can all contribute to non-indexed pages. These non-indexed pages can have a significant impact on your SEO, as they hinder your website’s visibility and decrease organic traffic. By using Google Search Console and crawling tools, you can identify non-indexed pages and then proceed to fix technical issues and optimize your content for indexing. Monitoring indexed pages and requesting reindexing are also essential in ensuring that your webpages are properly indexed. To prevent future issues, regular crawling and indexing checks, as well as XML sitemap optimization, are recommended. By following these steps, you can improve the indexing of your webpages and enhance your website’s overall SEO performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can non-indexed pages still receive organic traffic?
No, non-indexed pages cannot receive organic traffic because search engines are unable to include them in their search results.
2. How can I check if my pages are indexed?
You can check if your pages are indexed by using Google Search Console or by performing a site search on Google using the “site:” operator.
3. What should I do if I find non-indexed pages on my website?
If you find non-indexed pages on your website, you should first identify the reason behind it, such as technical issues or low-quality content. Once identified, you can take steps to fix the issues and optimize the pages for indexing.
4. How long does it take for a page to get indexed?
The time it takes for a page to get indexed can vary. It can take anywhere from a few hours to a few weeks for search engines to crawl and index a page.
5. Can I manually request search engines to index my pages?
Yes, you can manually request search engines to index your pages by submitting the URL through Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool or by using the “Fetch as Google” feature.
6. How can I fix technical issues that prevent indexing?
To fix technical issues that prevent indexing, you should ensure that your website is accessible to search engine bots, check your robots.txt file for any blocking directives, and fix any server errors that may be affecting crawlability.
7. What are some strategies for optimizing content for indexing?
Some strategies for optimizing content for indexing include using relevant and descriptive titles, meta tags, and headers, incorporating keywords naturally throughout the content, and ensuring that the content is unique and valuable to users.
8. How often should I monitor my indexed pages?
It is recommended to regularly monitor your indexed pages to ensure they are still appearing in search results and to identify any issues that may have caused them to become non-indexed.
9. Can XML sitemaps help with indexing?
Yes, XML sitemaps can help search engines discover and crawl your webpages more efficiently, increasing the chances of them being indexed.
10. How can I prevent future indexing issues?
You can prevent future indexing issues by regularly checking for technical issues, optimizing your content for indexing, regularly updating and adding new content, and submitting updated XML sitemaps to search engines.